The second sensor covered in these posts is the analog electrical conductivity (EC) sensor. It has a very similar usage to the pH sensor, both being analog and accompanied by buffer solutions.

The EC sensor will be used to measure the electrical conductivity of a body of water. EC is an important characteristic in water monitoring, because it reflects the number of electrolytes present in the water. Its value isn’t the most important as is, but we can determine the an approximate value that represents the total dissolved solids (TDS) in the water, because EC and TDS are proportional to each other [1]. A high value of TDS usually means that the water has a lot of contaminants.
Salt and other inorganic chemicals the EC of water. Below is a picture that shows the TDS value in parts per million for different purities of water:
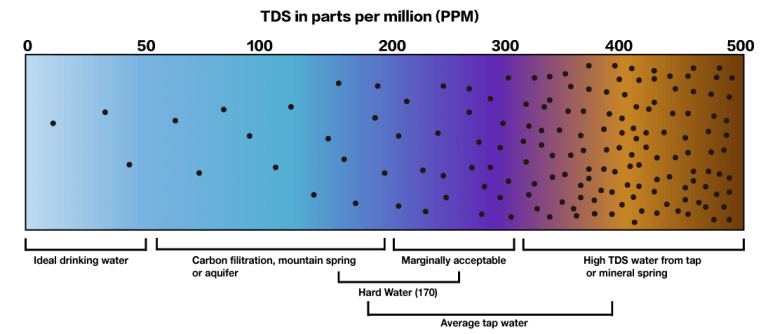
Therefore, we can use the EC sensor as a TDS sensor to be able to measure how contaminated the water is. The buffer solutions come in two sets of 2 bottles. The first set is of 1413uS/cm conductivity and the second is of 12.88mS/cm conductivity. It is usually measured in siemens, noted S, a standard SI unit. These solutions will be useful to calibrate the sensor, just like the method used for the pH sensor.
Sources
[1] DFRobot, “Gravity: Analog Electrical Conductivity Sensor /Meter V2 (K=1)”, DFRRobot. [Online]. Available: https://www.dfrobot.com/product-1123.html
[2] Ains, “Build Your Own Water Quality Monitoring Station with 5 Water Quality Sensors”, Seeedstudio, June 2020. [Online]. Available: https://www.seeedstudio.com/blog/2020/07/06/build-your-own-water-quality-monitoring-station-with-5-water-quality-sensors-m/

